A new study has found that for every e-cig pod not purchased as a result of raising taxes on vaping, 6.2 additional packs of cigarettes will be sold on average.
New research published in the FASEB Journal has found that smoking cigarettes disrupts the body’s internal clock in both the brain and lungs, leading to a decrease in overall activity and disturbance of the sleep cycle in the mice studied.
A paper from Dr. Konstantinos Farsalinos and Prof. Gerry Stimson tackles the question of whether medical regulation for electronic cigarettes is justified.
If there was one rule for conducting scientific studies on a topic, it would be to make sure you understand it first. But with e-cigarettes, that is not what happens. All too frequently, vaping researchers know almost nothing about vaping, and the result is invariably a study that ends up discouraging smokers from making the switch. Here are some of the worst offenders.
A new study from Dr. Konstantinos Farslinos and colleagues has provided further confirmation that e-cigarettes are vastly safer than cigarettes, including naturally-extracted tobacco (NET) e-liquids that use flavor directly extracted from tobacco leaves. Among other findings, NET e-liquids were shown to have over 200 times less nitrosamines than cigarettes.
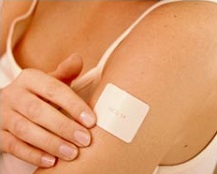
A new study published in Lancet from researchers in New Zealand has pitted e-cigarettes against patches to see which approach is more effective.
It shouldn't come as a surprise that a recent study found that teenagers are using e-cigarettes to vape pot. The headline finding is that almost one in five teens who’d tried vaping e-liquid had also tried vaping marijuana, but – as always – such an opportunity couldn’t be allowed to pass by without attempting to blame e-cigarettes for what happened. So, are e-cigarettes a gateway to marijuana now?
A new study claims to have found that watching ads for e-cigarettes featuring the act of vaping increases the urge to smoke for daily smokers and weakens intentions to continue abstaining for ex-smokers. However, taking a look at the details makes it obvious that this study must be interpreted with caution.
Are second generation e-cigs more effective for quitting than cig-a-likes? The latest clinical trial answers with an emphatic "yes": finding that second-gen e-cigs significantly reduce cravings and many smokers – even ones with no intention of quitting – successfully kick their combusted tobacco habit.
A new study from the UK has found that the number of 10 to 11 year olds who’d ever tried e-cigarettes was actually higher than the corresponding number for tobacco cigarettes, with the researchers arguing the finding "reinforces concerns" about a potential gateway to smoking.
A new UCSF study headed by Stanton Glantz has concluded that e-cigs don't aid in smoking cessation. So how did they come to this conclusion?
Are teens who try e-cigarettes more likely to try tobacco cigarettes? Stanton Glantz believes e-cig use may promote smoking.
A new study claims to have found carbon monoxide in e-cigarette vapor, and the news media is sounding the alarm: but is it a genuine concern? With echoes of the formaldehyde story from years ago, the answer is a resounding "no."
If you want a constant stream of junk science on a topic, one thing you’ll need is some researchers willing to crank out a shoddy paper in support of your cause, ideally without putting too much work into it. And the University of North Carolina's Rebecca Williams has mastered the art.
A new survey of Minnesota-based middle and high school students has provided further evidence that the potential gateway to smoking is not a genuine concern, but, as is the pattern with such studies, it’s being presented as showing the exact opposite.
New data from ASH UK has shown that – much like in the US – the false belief that e-cigarettes are as dangerous as or more dangerous than smoking is becoming more common in both smokers and the general population. The implication is depressingly clear: frequent misleading statements about e-cigarettes are discouraging smokers from switching to the reduced harm alternative.
A new study has offered further evidence of the harm reduction potential of e-cigarettes, finding that e-cig vapor is less toxic to lung cells than cigarette smoke, and that it also produces less oxidative stress.
After the release of a new study looking at formaldehyde in e-cig vapor, the media has gone into a predictable frenzy of fearmongering. But what does the evidence really say?
Many companies have cropped up in recent years touting the benefits of vaping vitamins, but is it really a good idea? Will it work? Is it safe? Here's what you need to know.
The picture frequently painted for the public is that nicotine alone creates the addiction to smoking, and that nicotine in itself – whether consumed by smoking or vaping – is hugely addictive. But is this really true? Here's everything you need to know about e-cigarettes and nicotine addiction.