Meditation is arguably one of the most popular and arguably most effective stress-relievers in the world. Many people practice meditation techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and focused attention to manage pain and inflammation symptoms, diminish anxiety and depression, and promote inner health and wellbeing.
These techniques, as well as others, have been practiced throughout the millennia. Archaeologists believe the art of meditation dates back to as early as 5000 BCE, around the same time as the Neolithic period
Now, with the advancements in technology and our scientific understanding of human biology, we’re beginning to understand how meditation affects us physiologically — or, more specifically, how it positively affects our endocannabinoid system.
Let’s take a closer look.
At a glance:
- Your endocannabinoid system is a complex system composed of three components: cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes. These components work together to bring your body to a state of balance and harmony
- Meditation combats stress, anxiety, and negative thinking (three things known to harm your endocannabinoid system)
- Meditation and cannabis (hemp or marijuana) can enhance your meditation sessions — CBD specifically targets certain receptor sites resulting in anti-inflammation, pain relief, and anxiety reduction
- Full-spectrum hemp-derived CBD products recommended. Best cannabinoids for meditation = CBD, THC, CBN, CBC, CBG, CBDA. Best terpenes for meditation = myrcene, linalool, beta-caryophyllene, and nerolidol. All combined = greater effects and benefits.
- Other ways to support your endocannabinoid: healthy foods, exercise, & cold exposure
What is the endocannabinoid system?
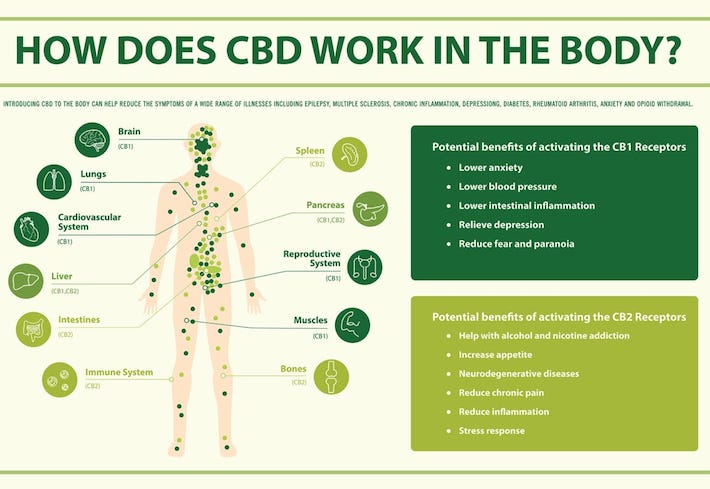
The endocannabinoid system (often abbreviated to ECS) is a complex biological system found in all vertebrates (mammals, reptiles, fish, and birds) and a large percentage of invertebrates (urchins, leeches).
This system is composed of three main components: cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes.
Cannabinoid receptors
There are two main cannabinoid receptors in your body aptly named cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while your CB2 receptors are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system and immune cells.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids, which are very clever neurotransmitters produced within your own body, binds to both receptors, signaling the endocannabinoid system to respond to whatever problem is happening inside you.
The two primary endocannabinoids in your system are anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). The shape of these endocannabinoids is very similar to cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
When you consume cannabis or cannabis-related products, CBD and THC, as well as other beneficial plant compounds, act upon your cannabinoid receptors to boost endocannabinoid production. Other receptor sites are targeted as well such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), serotonin (5-HT1A), and dopamine.
This endocannabinoid boost essentially promotes a healthier endocannabinoid system and, by extension, improves your overall physiological health and wellbeing.
Enzymes
Enzymes remove the endocannabinoids from the target area(s), preventing them from overstaying their welcome.
The two primary enzymes are fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol acid lipase (MAGL).
FAAH is responsible for the breaking down of AEA endocannabinoids, while MAGL is responsible for breaking down of 2-AG endocannabinoids.
What is the overall function of the endocannabinoid system?
As a trio, these components ultimately help regulate and maintain your body’s core functionality.
Core functions include:
- Sleep
- Mood
- Memory
- Appetite
- Pain response and management
- Inflammation
- Reproductive function
In other words, your endocannabinoid system (with the help of cannabis!) works to bring your body to a state of physiological balance and wellbeing, otherwise known as homeostasis.
Meditation can help boost your endocannabinoid system (without consuming cannabis)

As mentioned, consuming cannabis and its chemical compounds (CBD, THC, terpenes) can give your endocannabinoid system a much-needed revival.
However, it’s understandable not everyone walking this great green earth wants to put cannabis inside them, irrespective of whether it’s a hemp or marijuana-derived product.
Some people believe cannabis compounds may cause long-term health problems (which isn’t accurate but that’s another story for another time).
Meditation is a great alternative. No external substances or intoxicating compounds. Just you, your mind, and your body working together in a blissful journey towards personal enlightenment.
Here’s why meditation on its own is great for your endocannabinoid system
Many practice meditation to reduce stress, combat anxiety, and clear the mind of any worrying or negative thoughts.
Chronic stress and anxiety are said to cause havoc on your endocannabinoid system, resulting in reduced endocannabinoid levels and suppressed CB1 receptor activity, specifically in the brain’s hippocampus.
Studies show reduced endocannabinoid levels and CB1 receptor activity in the hippocampus caused by stress could lead to psychiatric disorders such as severe depression and anxiety.
Luckily, stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises (combined or on their own) produce mild-to-moderate cannabimimetic effects and benefits.
In other words, meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing have the same (but milder) effects and benefits as cannabis compounds such as CBD, THC, etc.
It’s therefore plausible to suggest cannabis and meditative practices are somewhat similar in terms of how they benefit you physiologically.
So, what happens if you consume cannabis and meditate?
Consuming cannabis to heighten your meditative experience (if you want to)

There are no rules here. If you want to consume cannabis and meditate at the same time, go for it!
Many users believe consuming THC-rich marijuana flower, capsules, or oil helps meditative focus and concentration. The “high” they experience enhances the journey, allowing the mind and body to fully release from daily stresses.
Other people stay away from high-THC marijuana and consume hemp-derived low-THC, high-CBD products instead. We personally believe hemp-derived is better, simply because there’s no intoxication and you are in total control of your own meditation practices.
What’s the link between cannabis and meditation?
Hemp-derived CBD products carry a high percentage of CBD with very little THC. The higher the CBD content, the more likely you are to experience the beneficial effects in combination with meditation.
The way CBD works in your body is conducive to an enhanced meditation experience. Unlike THC, CBD is known to indirectly interact with your endocannabinoid system via other receptor sites, most notably 5-HT1A (hydroxytryptamine) serotonin receptors and TRPV1 vanilloid receptors.
CBD’s interaction with serotonin receptors for meditation
CBD’s affinity with serotonin receptors is important, especially in the realm of meditation.
Serotonin receptors are located throughout the central nervous and peripheral nervous system. Researchers believe CBD’s activation of these receptors results in quite a significant reduction in anxiety, stress, and depression.
Together, these benefits are crucial to physiological and psychological balance. Paired with the serenity of meditation, you’re onto a sure-fire winner.
CBD’s interaction with vanilloid receptors for meditation
CBD’s interaction with vanilloid receptors is also very important for meditation.
You may notice the name is similar to “vanilla”. This isn’t a coincidence. Vanilloid receptors are named after the vanilla bean, a famous spice known to carry antioxidant, antiseptic, and analgesic properties.
When CBD binds to these receptors, it causes a strong antihyperalgesic effect without cannabinoid receptor involvement. In other words, CBD has the ability to manage severe pain and inflammation symptoms without targeting CB1 or CB2.
The great thing about this interaction is it can soothe any pain you may have while meditating, causing no unwanted distractions.
To get the best out of your meditation session, we recommend a full-spectrum hemp extract
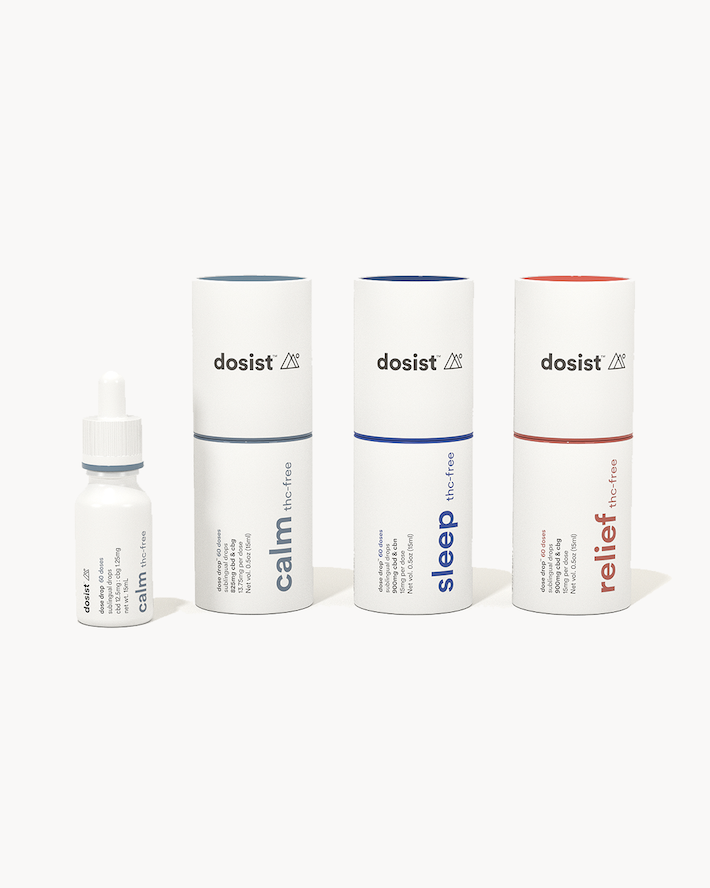

If you’re going to purchase hemp-derived CBD products, make sure it carries a full-spectrum hemp extract. Full-spectrum hemp extracts contain a full range of valuable plant compounds such as CBD and THC (of course), as well terpenes, flavonoids, alcohols, and lipids.
Combined, these plant compounds work in synergy, producing what’s known as the entourage effect for enhanced effects and benefits.
The best cannabinoids for meditation include:
Cannabinol (CBN)
CBN is a powerful cannabinoid, especially when paired with CBD and THC. It’s known to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and act as a relaxing sleep aid (with THC).
Cannabichromene (CBC)
CBD is another powerful cannabinoid known to produce quite potent anti-anxiety and antidepressant benefits, as well as some pain-relieving effects when combined with CBD.
Cannabigerol (CBG)
CBG is one of the most important cannabinoids in varieties of cannabis. Said to combat signs of inflammation, tackle pain symptoms, and reduce nausea (with CBD).
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA)
CBDA is CBD’s precursor acid. Higher quantities are typically found in raw, untouched hemp. You won’t commonly find it in hemp-derived CBD oils or capsules due to decarboxylation during extraction. The best way to consume high levels of CBDA is to “juice” raw hemp i.e. blend and consume it as a beverage.
CBDA is said to act upon serotonin receptors the same way as CBD, producing potent anti-anxiety and anti-stress relief.
The best terpenes for meditation include:
Myrcene
Myrcene is the most common terpene present in varieties of cannabis. Full-spectrum extracts carry a large percentage. Known for its peppery and spicy aroma. Research shows myrcene is a potent muscle relaxant and sedative capable of being a significant sleep aid (in higher doses). Also good for inflammation and pain-relief.
Beta-caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene (often shortened to caryophyllene) is very common in cannabis. Typically found in high quantities. Strong spicy aroma. Therapeutically, caryophyllene is a good all-rounder. Known for its anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving, and antioxidant qualities. Carries potent anti-anxiety and antidepressant properties.
Linalool
Linalool is less abundant in cannabis than myrcene. Full-spectrum hemp extracts carry a small percentage (usually trace amounts). Citrusy and sweet aroma. Smelling myrcene’s odor is believed to activate GABA receptors in the central nervous system via olfactory neurons in the nose. This activation results in physiological relaxation. When consumed, linalool may promote anti-stress and anti-anxiety qualities.
Nerolidol
Nerolidol (also known as peruviol and penetrol) is a lesser-known terpene with a lot of firepower. Found in low percentages compared to myrcene and caryophyllene. Aromatically similar to fresh bark/wood with a slightly floral and rose-apple scent. Studies show nerolidol’s sedative qualities for optimal relaxation before and after meditation.
If you prefer high-THC marijuana consumption when meditating, choose these strains
Not all high-THC marijuana strains are created equal. Some are known to induce energy and hyperfocus, while others are said to produce lethargy, laziness, and fatigue.
Picking the right one for clearer-minded meditation is a struggle, so we recommend the following:
- Northern Lights (Indica) — calming, mellowing, not too potent but enough to keep you in a zen-like state
- Lamb’s Bread (Indica) — can be quite energizing but has a feeling of introspection and tranquility along with it
- Jack Flash (Hybrid) — mood-enhancing, uplifting, and euphoric without being too energizing, will keep you pretty level-headed and focused on your thoughts and body
TIP: When consuming high-THC marijuana strains, make sure not to go overboard with it. Consume a quarter of your regular dose to avoid being way too baked to even sit up straight. Microdosing cannabis is the preferred choice here. Nice and steady. No need to rush.
We recommend smoking, vaping, or dabbing cannabis (marijuana or hemp) for the best meditation results
There are many different ways of delivering cannabis into your body. Some good, some not so good.
We personally believe smoking, vaping, or dabbing cannabis (marijuana or hemp) are the best avenues to take if you want the best experience. All three delivery methods are the most effective.
The reason?
Inhalation of cannabis goes straight into the bloodstream via your lung’s microcapillaries. The effects are pretty much instantaneous.
The difference between inhalation and oral consumption of, say, cannabis edibles is bypassing the digestive system.
Cannabis compounds (THC, CBD, etc) avoid being broken down and metabolized by the liver, a process known to reduce the total amount absorbed into the bloodstream. This lower absorption rate results in less beneficial physiological effects and benefits.
In other words, inhalation of cannabis provides you with a fast-acting, well-rounded experience.
We recommend marijuana-derived/hemp-derived CBD flower or concentrates (shatter, wax, live resin). If you’re a beginner, cannabis pre-rolls and cigarettes are a great start.
Make sure to purchase a high-quality weed vaporizer if you’re looking to vape or dab cannabis.
Other ways to give your endocannabinoid system a boost (without consuming cannabis)

Endocannabinoid system-boosting foods
Endocannabinoid system-boosting food includes chocolate, herbs, spices, tea, and essential fatty acids.
Essential fatty acids
Essential fatty acids (EFAs) such as omega-3 and 6 are, well, essential to a functioning endocannabinoid system, though balance is vital. Heavy consumption of EFAs can downregulate cannabinoid receptors and contribute to cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Over-consumption of omega-6 can cause inflammation as well.
Foods rich in EFAs include:
- Hemp seeds and hemp seed oil*
- Eggs
- Salmon and sardines
- Flax seeds and oil
- Chia seeds
*REMEMBER: Hemp seeds and hemp oil are not the same as hemp-derived CBD edibles and CBD oils. Hemp seed oil (also known as hemp oil) is made from the seeds of hemp, as opposed to fully grown hemp plants. While there are cannabinoid compounds in hemp seed oil, the overall percentage is nowhere near the same as hemp-derived CBD products. Doesn’t produce the entourage effect or the same therapeutic benefits.
Chocolate
Chocolate contains cocoa powder derived from cacao beans. Cacao powder carries three value compounds that are structurally similar to the body’s endocannabinoids. The compounds inhibit endocannabinoid metabolism, causing higher levels to remain throughout your body.
If you do consume chocolate with cannabis, researchers believe there’s an enhancement of effects due to the increase of anandamide levels in the central nervous system.
Avoid these foods for a healthier and better-functioning endocannabinoid system
- Processed and refined sugars
- Processed grains
- Alcohol (chronic and excessive use)
- Deep fat fried food
Pounding the pavement (and other stress-relieving activities)
Your endocannabinoid system thrives on a stress-free environment to keep it working efficiently. Alongside eating endocannabinoid-enhancing foods, we recommend fun but physically demanding activities.
Studies show moderately-intense exercise can significantly boost your endocannabinoid system, resulting in a fast-acting and long-lasting production of mood-enhancing endocannabinoids for up to 30 minutes.
Moderate-intensity physical activities or workouts include:
- Light running
- Cycling
- Swimming (low impact)
- Dancing
- Hiking
- Doubles tennis
- Ice skating
Socializing is also a helpful solution to endocannabinoid system health. Being with your buddies can help alleviate stress by distracting you from worrying thoughts. Studies show socializing during a tough period at work can reduce acute symptoms of anxiety and depression, irrespective of whether you’re extraverted or not.
Just remember: if you’re socializing with alcohol, be careful. High doses of acute and chronic alcohol consumption are known to decrease AEA endocannabinoid activity in the brain, leading to cognitive impairment and some psychological problems, especially when hungover.
Exposing yourself to the cold (it really does help!)
Surprisingly, exposing yourself to very cold temperatures increases endocannabinoid production, as well as increase CB1 immunopositive neurons density by up to 40%.
If you live in a country with a very cold climate and you have a near-frozen lake near you, take a plunge. The cold temperatures will boost endocannabinoid activity. If you live in a warmer climate, a cold shower is more than enough to get your endocannabinoids working.


